Spring 源码第二弹!XML 文件解析流程
Spring 源码继续开整!
上篇文章中,松哥和大家分享了 Spring 中配置文件的加载方式,如果小伙伴们还没看过,一定先看一下,这有助于更好的理解本文,传送门:Spring 源码第一篇开整!配置文件是怎么加载的?。
上篇文章和大家分享了 Spring 中是如何加载本地配置文件的,如何将加载到的本地配置文件通过一个 InputStream 返回。了解到这一点之后,接下来就是对 InputStream 的解析了。
本文我们就来看一下整个解析流程是什么样子的。
1.XmlBeanDefinitionReader
在上篇文章中,小伙伴们可以看到,XmlBeanFactory 中加载 XML 文件流的对象是 XmlBeanDefinitionReader,因此关于 XML 的解析我们就从 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 开始讲起。
先来看一张 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的继承关系图:
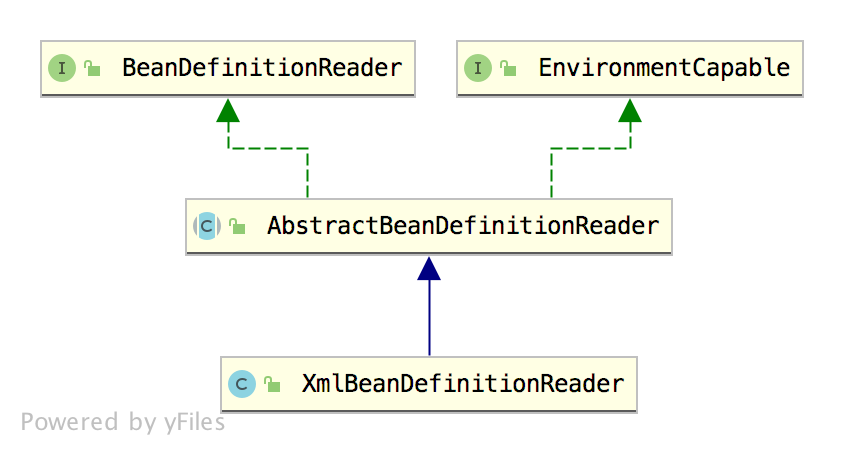
这张继承关系图中涉及到了几个接口,我这里和大家说一下:
- BeanDefinitionReader:这个接口主要定义了资源文件的读取并将资源转为 BeanDefinition。
- EnvironmentCapable:这个接口定义了获取 Environment 的方法。
- AbstractBeanDefinitionReader:实现了 BeanDefinitionReader 和 EnvironmentCapable 接口中所定义的方法。同时,AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 中多了一个比较关键的属性叫做 ResourceLoader,ResourceLoader 可以根据给定的资源返回对应的 Resource。
- XmlBeanDefinitionReader 则在 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 的基础上继续扩展了它的功能。
这是 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的继承关系。
打开 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的源码,我们发现还有两个关键的对象:
- BeanDefinitionDocumentReader:BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 接口只有一个实现类就是 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader ,在这里定义了对 Document 对象的读取并将读取到的属性转为 BeanDefinition。
- DocumentLoader:将资源文件转为 Document 对象。
担心有的小伙伴可能不知道 Document 是啥,我这里再稍微说两句。Document 就是 XML 解析时获取到的文档对象,Document 对象代表了一个 XML 文档的模型树,所有的其他 Node 都以一定的顺序包含在 Document 对象之内,排列成一个树状结构,以后对 XML 文档的所有操作都与解析器无关,直接在这个 Document 对象上进行操作即可。主流的 XML 解析方式有 SAX 解析、DOM 解析以及 Pull 解析。如果大家对于 XML 文件解析不熟悉的话,可以自行复习,松哥这里就不再啰嗦了。
好了,了解了 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的继承关系以及里边定义的两个关键类之后,我们来大概梳理一下 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的功能:
- 首先 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 继承自 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader,利用 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 中的 ResourceLoader 将配置文件路径转为对应的 Resource。
- 接下来,利用 DocumentLoader 将 Resource 转为 Document。
- 最后,利用 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 去解析 Document。
把这些先搞清楚之后,接下来我们来走流程。
2.走流程
不知道还记不记得上篇文章中松哥给出的一个简单案例:
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
我们就跟着 XmlBeanFactory 的构造方法来走一遍。
先来看 XmlBeanFactory 的构造方法:
1 | public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory { |
XmlBeanFactory 的源码很简单,其实它的主要功能都在 DefaultListableBeanFactory 中实现了,松哥后面会专门写一篇文章来介绍 DefaultListableBeanFactory,这里我们先不做过多展开。
XmlBeanFactory 中定义了 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 用来读取 Resource,默认情况下,parentBeanFactory 为 null,具体的读取操作则是由 XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions 方法提供的,我们来看下该方法:
1 |
|
- 在 loadBeanDefinitions 方法中,首先会将传入的 Resource 转为一个 EncodedResource,也就是对传入的资源进行编码,所谓的编码大家不要想的过于复杂,其实就是在将来读取资源的时候添加一个编码格式的参数,具体可以参见 EncodedResource#getReader 方法,因为比较简单,我这里就不贴出来了。
- 继续调用另外一个重载的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法,传入编码后的资源。
- 首先将当前资源添加到一个 ThreadLocal 中,这样可以避免重复加载。
- 将 XML 配置文件的 IO 流转为一个 InputSource 对象,InputSource 是 XML 文件解析的起点,XML 文件解析这块大家自己复习下,松哥就不做过多介绍了。
- 如果资源有编码格式,那就给 inputSource 对象也设置上编码格式。
- 调用 doLoadBeanDefinitions 方法做进一步的解析操作。
- 最后从集合中移除资源。
在上面第 6 步的时候,调用了 doLoadBeanDefinitions 方法,这个方法要做的事情就是去将资源文件解析成 Document 对象,如下:
1 | protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) |
可以看到,这里就是调用 doLoadDocument 进行资源解析,最终获取到一个 Document 对象。
我们来看一下 doLoadDocument 方法:
1 | protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception { |
可以看到,这里最终调用的是 documentLoader#loadDocument 方法,documentLoader 也就是松哥在第一小节和大家介绍的 DefaultDocumentLoader 对象。
该方法的调用,一共需要五个参数:
- 第一个 InputSource 不用多说,这是要调用的资源文件。
- 第二个 EntityResolver 主要是处理文件的验证方式的。
- 第三个 ErrorHandler 是一个错误处理器。
- 第四个 validationMode 是指 XML 文件的验证模式。
- 第五个 namespaceAware 表示是否开启自动感知名称空间。
具体的调用如下:
1 | public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver, |
这里我就不做过多解释了,基本上到了 XML 解析的范畴了。小伙伴们自行复习一下 Java 中 XML 的解析方式。
3.小结
本文松哥主要和大家介绍了在 Spring 中,我们如何获取到一个 Document 对象,拿到 Document 对象,接下来解析 Document 对象,获取各种属性,就能定义出 BeanDefinition 了。
但是如果大家从来没有研究过 Spring 源码,相信本文中可能还有很多让你疑惑的地方,例如 EntityResolver 到底是干嘛用的?ValidationMode 又是啥?那么小伙伴们不要着急,这些东西松哥会在接下来的文章中像大家挨个介绍。
好啦,今天就先说这么多,如果大家觉得有收获,记得点个在看鼓励下松哥哦~
