手机短信登录、邮箱登录、QQ 登录都想要,咋办?
[TOC]
今天想和大家聊一聊 Shiro 中的多 Realm 认证策略问题~
在项目中,如果我们想手机验证码登录、第三方 QQ 登录、邮箱登录等多种登录方式共存,那么就可以考虑通过 Shiro 中的多 Realm 来实现,具体操作中,一个 Realm 刚好就对应一种登录方式。
多 Realm 登录的用法并不难,松哥之前也专门发过相关的文章和大家分享,传送门:
今天我不想聊用法,主要是想和大家聊一聊这里相关的源码。因此本文需要大家有一定的 Shiro 使用经验,若无,可以参考上面的链接恶补一下。
1. ModularRealmAuthenticator
1.1 Realm 去哪了?
我们配置的 Realm,可以直接配置给 SecurityManager,也可以配置给 SecurityManager 中的 ModularRealmAuthenticator。
如果我们是直接配置给 SecurityManager,那么在完成 Realm 的配置后,会自动调用 afterRealmsSet 方法,在该方法的中,会将我们配置的所有 Realm 最终配置给 ModularRealmAuthenticator。
相关源码如下:
RealmSecurityManager#setRealm(RealmSecurityManager 是 DefaultWebSecurityManager 的父类)
1 | public void setRealm(Realm realm) { |
可以看到,无论是设置单个 Realm 还是设置多个 Realm,最终都会调用到 afterRealmsSet 方法,该方法在 AuthorizingSecurityManager#afterRealmsSet 类中被重写,内容如下:
1 | protected void afterRealmsSet() { |
可以看到,所有的 Realm 最终都被设置给 ModularRealmAuthenticator 了。
所以说,无论是单个 Realm 还是多个 Realm,最终都是由 ModularRealmAuthenticator 统一管理统一调用的。
1.2 ModularRealmAuthenticator 怎么玩
ModularRealmAuthenticator 中核心的方法就是 doAuthenticate,如下:
1 | protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { |
这个方法的逻辑很简单:
- 首先调用 assertRealmsConfigured 方法判断一下开发者有没有配置 Realm,要是没有配置就直接抛异常了。
- 判断开发者配置了几个 Realm,要是配置了一个,就调用 doSingleRealmAuthentication 方法进行处理,要是配置了多个 Realm 则调用 doMultiRealmAuthentication 方法进行处理。
配置一个 Realm 的情况比较简单,不在本文的讨论范围内,本文主要是想和大家讨论多个 Realm 的情况。
当存在多个 Realm 的时候,必然又会带来另一个问题:认证策略,即怎么样就算认证成功?一个 Realm 认证成功就算成功还是所有 Realm 认证成功才算成功?还是怎么样。
接下来我们来详细聊一聊这个话题。
2. AuthenticationStrategy
先来整体上看下,负责认证策略的类是 AuthenticationStrategy,这是一个接口,有三个实现类:
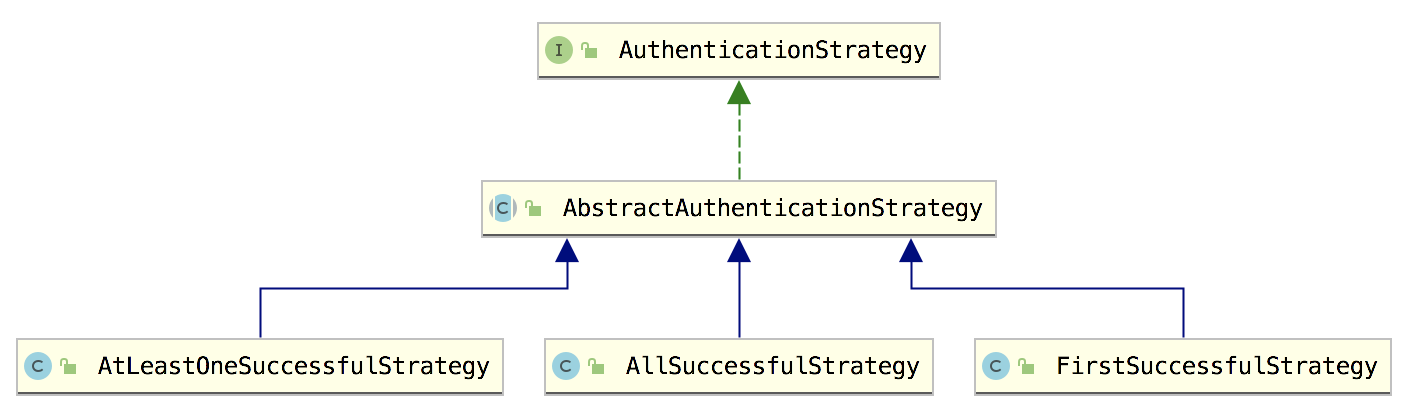
单从字面上来看,三个实现类都好理解:
- AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy:至少有一个 Realm 认证成功。
- AllSuccessfulStrategy:所有 Realm 都要认证成功。
- FirstSuccessfulStrategy:这个从字面上理解不太准确,它是只返回第一个认证成功的用户数据。
第二种其实很好理解,问题在于第 1 个和第 3 个,这两个单独理解也好理解,放在一起的话,那有人不禁要问,这俩有啥区别?
老实说,在 1.3.2 之前的版本还真没啥大的区别,不过现在最新版本还是有些区别,且听松哥来分析。
首先这里一共涉及到四个方法:
- beforeAllAttempts:在所有 Realm 验证之前的做准备。
- beforeAttempt:在单个 Realm 之前验证做准备。
- afterAttempt:处理单个 Realm 验证之后的后续事宜。
- afterAllAttempts:处理所有 Realm 验证之后的后续事宜。
第一个和第四个方法在每次认证流程中只调用一次,而中间两个方法则在每个 Realm 调用前后都会被调用到,伪代码就类似下面这样:

上面这四个方法,在 AuthenticationStrategy 的四个实现类中有不同的实现,我整理了下面一张表格,方便大家理解:

大家注意这里多了一个 merge 方法,这个方法是在 AbstractAuthenticationStrategy 类中定义的,当存在多个 Realm 时,合并多个 Realm 中的认证数据使用的。接下来我们就按照这张表的顺序,来挨个分析这里的几个方法。
2.1 AbstractAuthenticationStrategy
2.1.1 beforeAllAttempts
直接来看代码吧:
1 | public AuthenticationInfo beforeAllAttempts(Collection<? extends Realm> realms, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { |
这里啥都没干,就创建了一个空的 SimpleAuthenticationInfo 对象。
2.1.2 beforeAttempt
1 | public AuthenticationInfo beforeAttempt(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo aggregate) throws AuthenticationException { |
这个方法的逻辑也很简单,传入的 aggregate 参数是指多个 Realm 认证后聚合的结果,这里啥都没做,直接把结果原封不动返回。
2.1.3 afterAttempt
1 | public AuthenticationInfo afterAttempt(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo singleRealmInfo, AuthenticationInfo aggregateInfo, Throwable t) throws AuthenticationException { |
这是每个 Realm 认证完成后要做的事情,参数 singleRealmInfo 表示单个 Realm 认证的结果,aggregateInfo 表示多个 Realm 认证结果的聚合,具体逻辑如下:
- 如果当前 Realm 认证结果为 null,则把聚合结果赋值给 info 并返回。
- 如果当前 Realm 认证结果不为 null,并且聚合结果为 null,那么就把当前 Realm 的认证结果赋值给 info 并返回。
- 如果当前 Realm 认证结果不为 null,并且聚合结果也不为 null,则将两者合并之后返回。
2.1.4 afterAllAttempts
1 | public AuthenticationInfo afterAllAttempts(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo aggregate) throws AuthenticationException { |
这里直接把聚合结果返回,没啥好说的。
2.1.5 merge
1 | protected AuthenticationInfo merge(AuthenticationInfo info, AuthenticationInfo aggregate) { |
merge 其实就是调用 aggregate 的 merge 方法进行合并,正常情况下我们使用的 SimpleAuthenticationInfo 就是 MergableAuthenticationInfo 的子类,所以这里合并没问题。
2.2 AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy
2.2.1 beforeAllAttempts
同 2.1.1 小节。
2.2.2 beforeAttempt
同 2.1.2 小节。
2.2.3 afterAttempt
同 2.1.3 小节。
2.2.4 afterAllAttempts
1 | public AuthenticationInfo afterAllAttempts(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo aggregate) throws AuthenticationException { |
这里的逻辑很明确,就是当聚合结果为空就直接抛出异常。
2.2.5 merge
同 2.1.5 小节。
2.2.6 小结
结合 2.1 小节的内容,我们来梳理一下 AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy 的功能。
- 首先,系统调用 beforeAllAttempts 方法会获取一个空的 SimpleAuthenticationInfo 对象作为聚合结果 aggregate。
- 接下来遍历所有的 Realm,在每个 Realm 调用之前先调用 beforeAttempt 方法,该方法只会原封不动的返回聚合结果 aggregate。
- 调用每个 Realm 的 getAuthenticationInfo 方法进行认证。
- 调用 afterAttempt 方法对认证结果进行聚合处理。如果当前 Realm 认证返回 null,就把聚合结果返回;如果当前 Realm 认证不返回 null,就把 当前的 Realm 的认证结果和 aggregate 进行合并(aggregate 不会为 null,因为 beforeAllAttempts 方法中固定返回空对象)。
这就是 AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy 的认证策略。可以看到:如果只有一个 Realm 认证成功,那么正常返回,如果有多个 Realm 认证成功,那么返回的用户信息中将包含多个认证用户信息。
可以通过如下方式获取返回的多个用户信息:
1 | Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); |
subject.getPrincipals() 方法可以获取多个认证成功的凭证。
2.3 AllSuccessfulStrategy
2.3.1 beforeAllAttempts
同 2.1.1 小节。
2.3.2 beforeAttempt
1 | public AuthenticationInfo beforeAttempt(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException { |
可以看到,这里就是去检查了下 Realm 是否支持当前 token。
这块的代码我觉得略奇怪,为啥其他认证策略都不检查,只有这里检查?感觉像是一个 BUG。有懂行的小伙伴可以留言讨论下这个问题。
2.3.3 afterAttempt
1 | public AuthenticationInfo afterAttempt(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info, AuthenticationInfo aggregate, Throwable t) |
如果当前认证出错了,或者认证结果为 null,就直接抛出异常(因为这里要求每个 Realm 都认证成功,但凡有一个认证失败了,后面的就没有必要认证了)。
如果一切都 OK,就会结果合并然后返回。
2.3.4 afterAllAttempts
同 2.1.4 小节。
2.3.5 merge
同 2.1.5 小节。
2.3.6 小结
这种策略比较简单,应该不用多做解释吧。如果有多个 Realm 认证成功,这里也是会返回多个 Realm 的认证信息的,获取多个 Realm 的认证信息同上一小节。
2.4 FirstSuccessfulStrategy
2.4.1 beforeAllAttempts
1 | public AuthenticationInfo beforeAllAttempts(Collection<? extends Realm> realms, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { |
不同于前面,这里直接返回了 null。
2.4.2 beforeAttempt
1 | public AuthenticationInfo beforeAttempt(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo aggregate) throws AuthenticationException { |
这里的逻辑是这样,如果 getStopAfterFirstSuccess() 方法返回 true,并且当前认证结果的聚合不为空,那么就直接抛出异常,一旦抛出异常,就会跳出当前循环,也就是不会调用当前 Realm 进行认证操作了。这个思路和 FirstSuccessfulStrategy 名字基本上是契合的。
不过这里有一个方法 getStopAfterFirstSuccess(),看名字就知道是否在第一次成功后停止认证,默认情况下,该变量为 false,即即使第一次认证成功后,也还是会继续后面 Realm 的认证。
如果我们希望当第一次认证成功后,后面的 Realm 就不认证了,那么记得配置该属性为 true。
2.4.3 afterAttempt
同 2.1.3 小节。
2.4.4 afterAllAttempts
同 2.1.4 小节。
2.4.5 merge
不知道小伙伴们是否还记得 merge 方法是在哪里调用的,回顾 2.1.3 小节,如果当前 Realm 的认证和聚合结果都不为 null,就需要对结果进行合并,原本的合并是真正的去合并,这里重写了该方法,就没有去执行合并了:
1 | protected AuthenticationInfo merge(AuthenticationInfo info, AuthenticationInfo aggregate) { |
这是三个策略中,唯一重写 merge 方法的。
这里的 merge 并没有真正的 merge,而是:
- 如果聚合结果不为空,就直接返回聚合结果。
- 否则,如果当前认证结果不为空,就返回当前认证结果。
- 否则返回空。
可以看到,这里的 merge 其实就是挑选一个认证的 info 返回。如果前面有认证成功的 Realm,后面 Realm 认证成功后返回的 info 是不会被使用的。
2.4.6 小结
好啦,现在小伙伴们可以总结出 FirstSuccessfulStrategy 和 AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy 的区别了:
- AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy:当存在多个 Realm 的时候,即使已经有一个 Realm 认证成功了,后面的 Realm 也还是会去认证,并且如果后面的 Realm 也认证成功了,那么会将多个 Realm 认证成功的结果进行合并。
- FirstSuccessfulStrategy:当存在多个 Realm 的时候,默认情况下,即使已经有一个 Realm 认证成功了,后面的 Realm 也还是会去认证,但是如果后面的 Realm 也认证成功了,却并不会使用后面认证成功的 Realm 返回的结果。如果我们希望当一个 Realm 认证成功后,后面的 Realm 就不再认证了,那么可以配置 stopAfterFirstSuccess 属性的值,配置方式如下:
1 | <bean class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager" id="securityManager"> |
3. 小结
好啦,这就是松哥和大家分享的 Shiro 多 Realm 情况,感兴趣的小伙伴可以去试试哦~
公众号后台回复 shiro,获取 Shiro 相关资料。
